Altering Geometry
The built in Qkmaxware.Geometry.IMesh interface used to represent mesh based geometry throughout this library. ListMesh is a concrete implementation of this interface which uses a list as its storage structure and is immutable by nature. This means that alterations create new ListMesh instances rather than effecting the original mesh data.
Affine Transformations
In Qkmaxware.Geometry, affine transformations are represented using the Qkmaxware.Geometry.Transformation class. Transformations can then be applied to geometry by pre-multiplying the transformation to the mesh object. Transformations can be combined in sequence by pre-multiplying them.
Displacement
The displacement transformation is used to move geometry around 3d space. To create a displacement transformation, the Offset static constructor method of the Transformation class can be used to specify the displacement that you want to apply to a mesh.
var NewMesh = Transformation.Offset(new Vec3(3, 4, 5)) * OldMesh;
Scale
The scale transformation will shrink or grow geometry and can be created by the Scale static constructor method of the Transformation class.
var NewMesh = Transformation.Scale(2 * Vec3.One) * OldMesh;
Rotation
Rotation transformations will rotate a geometric object around 3D space. These transformations can be created by the Rx, Ry, Rz, and EulerRotation static constructor method of the Transformation class.
// Rotation around a specific axis
var NewMesh1 = Transformation.Rx(1.57) * OldMesh; // Rotate 90 degrees around the X axis
var NewMesh2 = Transformation.Ry(1.57) * OldMesh; // Rotate 90 degrees around the Y axis
var NewMesh3 = Transformation.Rz(1.57) * OldMesh; // Rotate 90 degrees around the Z axis
// Arbitrary rotation in 3D space
var NewMesh4 = Transformation.EulerRotation(new Vec3(1.57, 0.15, 3.2))
Custom Transformations
Besides each of the transformations above, you can define an arbitrary transformation using the Transformation class constructor. For this constructor the elements of the affine transformation matrix are directly provided. Below you can see how the matrix elements map to the constructor parametres.
| e01 | e02 | e03 | e04 |
| e11 | e12 | e13 | e14 |
| e21 | e22 | e23 | e24 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
var transformation = new Transformation(
e01, e02, e03, e04,
e11, e12, e13, e14,
e21, e22, e23, e24
)
Modifier Stacks
Geometry modifiers are non-destructive decorators which can be used to apply arbitrary modifications to geometry. Modifiers can be stacked to apply geometric modifications successively without damaging the original geometry,
Array
The array modifier, Qkmaxware.Geometry.Modifiers.Array, will repeat geometry multiple times moving them by a given amount on each repetition.
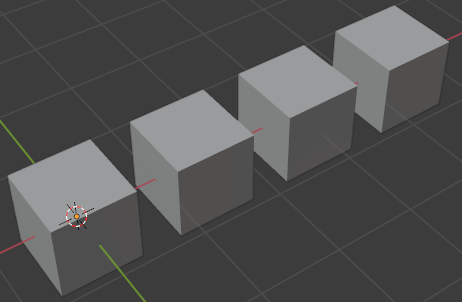
Path Deformation
The path deformation modifier, Qkmaxware.Geometry.Modifiers.PathDeform, will deform a geometry such that it follows a path.
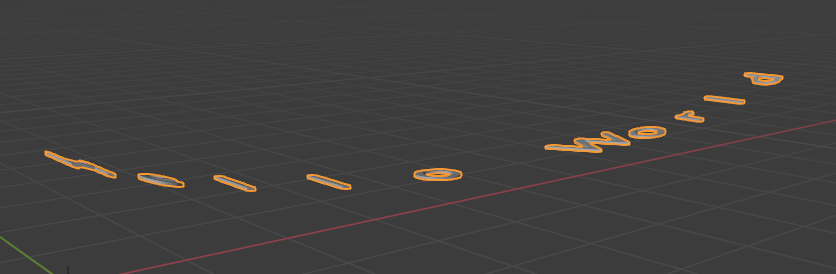
Mirror
The mirror modifier creates a new mesh that is mirrored across the given axis containing both the original triangles as well as the mirrored triangles.
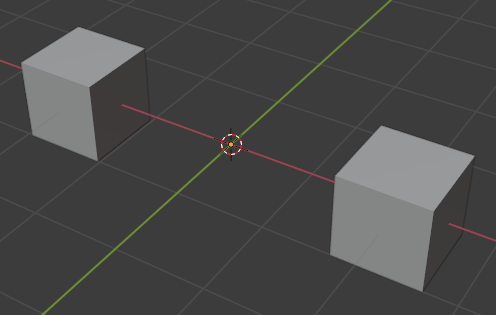
Subdivide
The subdivide modifier creates a new mesh in which each triangle has be sub-divided into 4 smaller triangles. This modifier can be used to increase the resolution of a given geometry.
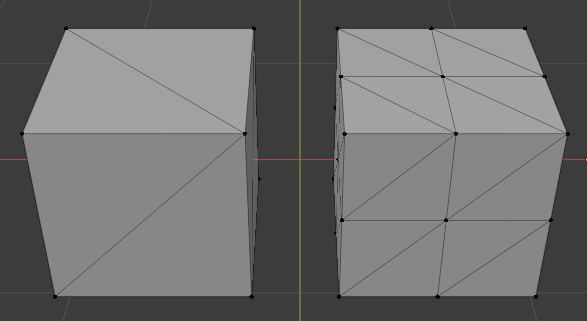
Scale
The scale modifier operates identically to the scale transformation. However, by being a modifier it does not allocate any additional mesh data until it is used whereas the transformation immediately creates a new mesh with the modified vertices.
Translate
the translate modifier operates identically to the offset transformation but as a modifier. This behaves the same as the scale modifier.
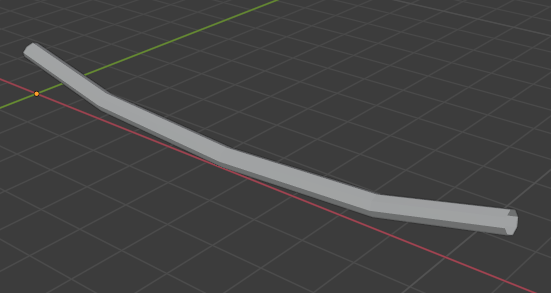
Path To Mesh
The path to mesh modifier creates a tube shaped mesh by following a path segment. Effectively this allows for one to convert a path object into a 3d mesh which follows the shape of the path.
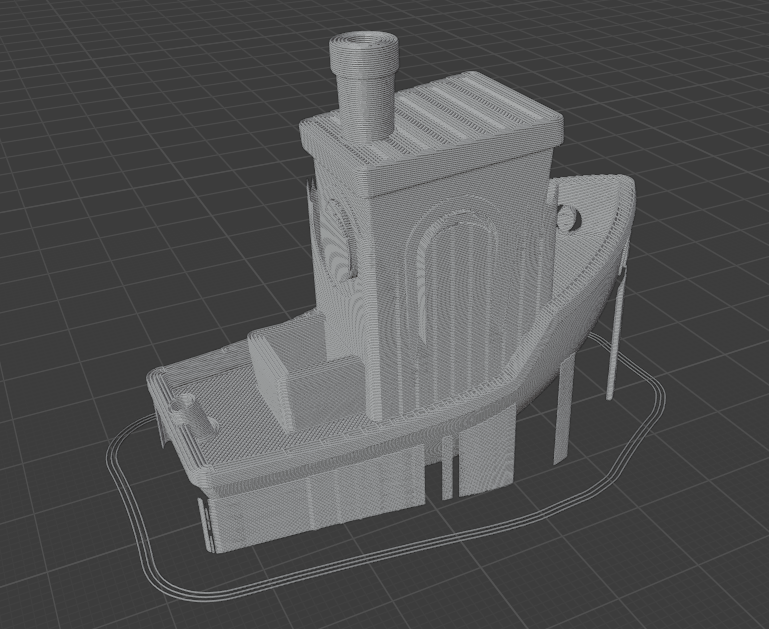
Render GCode
The render g-code modifier uses tubes to trace the path for a print-head of a 3D printer in order to convert 3D printer flavoured GCode back to a 3d model.
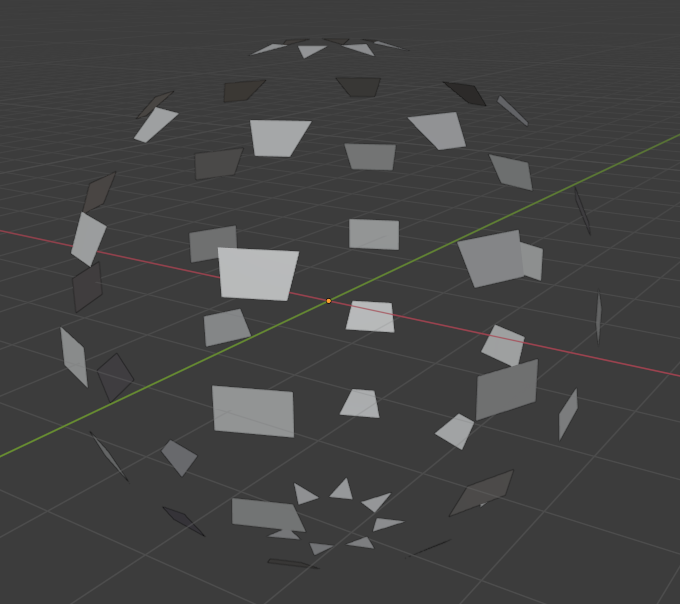
Explode
The explode modifier pushes the original triangles apart as if they were exploded outwards from their original locations.
Boolean Operations
Boolean operations are a set of operations common in the field of computer aided design. There are several different modifier which are capable of performing boolean operations.
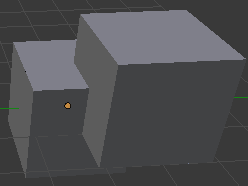
Union
the union modifier combines non-overlapping polygons from two geometry into a new geometry. Besides being offered as a modifier, this operation can also be done with the Union method of the ListMesh class, or by using the overloaded + operation.
Difference
the difference modifier is used to cut geometry out of a mesh where it overlaps with another geometry. Besides being offered as a modifier, this operation can also be done using the Difference method of the ListMesh class, or by using the overloaded - operation.
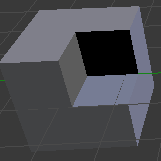
Intersection
The intersection modifier is used to save only the parts of a geometry where they overlaps with another geometry. Besides being offered as a modifier, this operation can also be done using the Intersection method of the ListMesh class, or by using the overloaded & operation.
Raw Triangles
If the above alteration methods do not work for your use case, you can create new geometry by looping over the individual triangles within a mesh and creating new triangles by altering the vertices.
IMesh CustomTransformation(IMesh mesh) {
List<Triangle> newTriangles = new List<Triangle>();
foreach (var triangle in mesh) {
var vertex1 = AlterVertex(triangle.Item1);
var vertex2 = AlterVertex(triangle.Item2);
var vertex2 = AlterVertex(triangle.Item3);
newTriangles.Add(new Triangle(vertex1, vertex2, vertex3));
}
return new ListMesh(newTriangles);
}